Driver for sending and receiving of SMS messages over GSM
mobile network
Driver features
The SMSDRV driver is intended for receiving and/or sending of
SMS messages over GSM mobile phones or dedicated GSM modems
connected through standard RS-232C serial interface. It is
possible to use for instance Siemens M1, M20, TC35 and MC35
modems, GSM modules made by Wavecom etc. Modem functions are also
supported by a number of GSM mobile phones -- for instance Siemens
S25, the whole x35 line, Nokia 6210, Alcatel OT 500 etc. Both PDU
and text message formats are supported.
List of sections: - Driver features
- Driver functionality
- Driver parameters
- Driver channels
- Driver procedures
- Driver Map File
- Driver exceptions
- Error codes
- Example of driver usage
Driver functionality
The driver can send a text message (SMS) to the defined
telephone number of the receiver. The maximum message length is
160 characters. The message should not contain special characters
not supported by the Short Message Service. It is necessary to
write the destination telephone number to the driver prior to
sending of the message. Then the message text itself is to be
written to the driver. The message is sent by writing of the
true value to the logical channel No. 8, which is
interpreted as the "send message" command. The driver raises
driver exception as the confirmation the operation finished. The
exception status defines if the operation was successful or
failed.
To detect message receiving, the driver periodically polls the
connected GSM device (modem or phone) and checks if some message
was received. If there is some newly received message, the message
text together with the sender telephone number is read and stored
to the queue. Then the message is deleted from the GSM device
memory and the driver exception is raised. The driver exception is
to be caught by some virtual instrument within the Control Web application. This virtual instrument should enable
next exception either by writing of the true value to the channel
No. 2 or by calling of the driver procedure EnableException.
Driver exceptions are also generated if the GSM device signaled
error during message sending of if the device stops responding at
all (e.g. is disconnected from the PC etc.).
Driver parameters
Driver behavior can be modified by settings of its
parameters. These parameters are defined in the '.PAR' file,
which is specified together with the driver in the Control Web application. PAR file is a text (ASCII) file, which can be
edited by a number of text editors (e.g. Notepad). Individual parameters
are grouped into several sections. Every section begins with a section
name, specified within square brackets. The parameter definition
follows, one parameter per line. Every line begins with parameter name,
followed by delimiter (character "=") and parameter
value.
Driver parameter definition — section [Settings]
This section contains parameters, which configures the
driver. Individual parameters and their possible values
are:
[Settings]
ComDriver = <driver>, <device>
InitString = <string>
SMSCenter = <string>
Timeout = <n>
MaxExceptions = <n>
ScanTime = <n>
DelayTime = <n>
ResetModem = true | false
Mode = PDU | TEXT
PassSMSCenter = 0 | 1 | 2
SendATZ = true | false
Validity = true | false
ReadSMSFrom = default | SM | MT
| driver | text string | | device | text string | | n | numeric value. |
Individual parameters description: | ComDriver | name of the driver library of the series
interface (link layers) and name of the communication port
(COMx) which is installed in the Windows environment.
The name of the standard driver is
'CWCOMM.DLL'. | | InitString | initialization string for the GSM modem. This string
is written to the device during modem initialization when
application starts or after some error is detected. This
string can be used e.g. to define SIM card PIN code
AT+CPIN="xxxx" (xxxx is PIN code; must be defined in
quotation marks). The initialization string can contain only
one AT command, but this AT command can contain settings of
more parameters. The driver does not support control
characters for line breaks (^M for CR). After sending of the
initialization string the driver sets additional modem
parameters, required for driver functionality (echo mode,
modem response format and SMS format, etc.). | | SMSCenter | number of the SMS center. The number must include the
state code (e.g. 420603052000 for the T-Mobile operator in
the Czech Republic). If this parameter is not specified, the
driver tries to obtain this number from the GSM device
before message is sent. | | Timeout | time of waiting for a response in
milliseconds. If during this time there is no device response, the
communication error will be returned into the application. Default value is 1000
ms. | | MaxExceptions | size of the queue for unprocessed
exceptions from the driver. The default setting is 4096. | | ScanTime | period of polling of the modem for newly received
messages in milliseconds. Default value is 3000 ms. | | DelayTime | time delay in milliseconds necessary to restart
modem. Default value is 3000 ms. | | ResetModem | this parameter enables automatic hardware modem
initialization using signals DTR and RTS after communication
error. Default value is true. | | Mode | this parameter defines message format — either PDU or TEXT. Default value is
PDU. | | PassSMSCenter | defines how SMS center number should be handled in
the PDU mode. Available parameters are: | 0 | SMS center number will be part of the
message | | 1 | number 0 will be used instead of SMS center
number | | 2 | SMS center number will be omitted |
| | SendATZ | enables sending of the AT command "ATZ" during modem
initialization. Default value is true. | | Validity | defines if the validity of the message in the PDU
mode will be limited to 24 hours. Default value is true. | | ReadSMSFrom | parameter defines the source from which messages
should be read. The following values are accepted. Available parameters are: | default | messages are read from modem default memory | | SM | messages are read from SIM | | MT | messages are read from modem memory |
Default value is SM (messages are read from
SIM). |
Example of the [Settings] section:
[Settings]
ComDriver=CWCOMM.DLL,COM1
Timeout=5000
MaxExceptions=100
ScanTime=10000
DelayTime=5000
ResetModem=false
PassSMSCenter=0
ReadSMSFrom=default
Communication link layer parameters — section [comm]
The
communication link layer represents a tool for access to the standard
serial interface of the computer. This layer makes it possible, among
other things, for one serial interface to be shared by more drivers. In
the Control Web system the communication link layer is
represented by two DLL libraries ('CWXLINK.DLL' and
'CWCOMM.DLL'). For its configuration in the parameter files
of the driver there is the section [comm]. Here you can
either define serial communication parameters directly or assign the
reference (redirection) to the independent configuration file with the
serial communication parameters. In the case of redirection, the section
[comm] contains only one parameter — file: [comm]
file=c:\cw\par\comm.par Structure of parameters of the link
layer: [comm]
file = <file>
device = <comdevice> If the parameter device
is defined and the section with the name comdevice exists
configuration parameters will be achieved with priority from this
section, otherwise parameters will be used directly from the section
[comm]. Mandatory parameters: [comm]
rx_frame_buffer = <N>
tx_frame_buffer = <N>
baudrate = <N>
databits = <N>
stopbits = one | 1 | oneandhalf | 1.5 | two | 2
parity = none | no | even | mark | odd | space
cts_flow = true | false
dsr_flow = true | false
dtr_control = disable | low | enable | high | handshake | toggle | toggle_neg
rts_control = disable | low | enable | high | handshake | toggle | toggle_neg
dsr_sense = low | high
rx_interchar_timeout = <N>
rx_char_timeout = <N>
rx_timeout = <N>
tx_char_timeout = <N>
tx_timeout = <N> Optional parameters: priority = idle | low | below_normal | normal | above_normal | high | realtime
mode = fullduplex | halfduplex
pre_key = <N>
hold_key = <N>
rx_buffer = <N>
tx_buffer = <N>
tx_continue_xon_xoff = true | false
tx_xon_xoff = true | false
rx_xon_xoff = true | false
xon_tresh = <N>
xoff_tresh = <N>
error_xlat = true | false
discard_null = true | false
xon_char = <N>
xoff_char = <N>
err_char = <N>
eof_char = <N>
evt_char = <N> Syntax categories: | file | file name at the parameter file | | comdevice | section name at the parameter device | | N | numeric value |
Description of individual parameters: | file | parameter file. It is advisable to use this parameter where
more drivers use a single link layer. Line parameters can then be
maintained in a single file. | | device | name, e.g.COM1. If this parameter is
specified, the device of this name will be used. If at the same time
there is a section with the same name, the following parameters will
be achieved from this section. If there is no section with this
name, parameters are read from the actual section.[comm]. | | priority | priority of the communication thread. The default value is
normal. | | mode | communication mode full duplex (bi-directional) or half
duplex (unidirectional). The default value is fullduplex. | | pre_key | delay in milliseconds before the starting of data
transmission. The status of DTR/RTS signals, if they work in toggle
mode, is changed during the delay to active. | | hold_key | delay in milliseconds after data transmission termination.
DTR/RTS signals , if they work in toggle mode, remain active during
the delay period. | | rx_frame_buffer | size of the secondary buffer for input. Permitted range
<96;65535>, the parameter does not have a default
value. | | tx_frame_buffer | size of the secondary buffer for output. Permitted range
<96;65535>, the parameter does not have a default
value. | | rx_buffer | size of the buffer for input; range <96;65535>, the
default value is 4096. | | tx_buffer | size of the buffer for output; range <96;65535>, the
default value is 4096. | | baudrate | communicating speed. | | databits | number of data bits. | | stopbits | number of stop bits. | | parity | parity of the transfer. | | cts_flow | enables CTS control (handshake) | | dsr_flow | enables DSR control (handshake) | | dtr_control | | | rts_control | behavior of DTS and RTS, meaning of values: | disable | control is off, permanently at low level | | low | works the same as disable | | enable | control is off, permanently at high level | | high | works the same as enable | | handshake | positive handshake | | toggle | the status of the signal is changed during data
transmission to high (positive key), otherwise permanently in
low | | toggle_neg | the status of the signal is changed during data
transmission to low (negative key), otherwise permanently in
high |
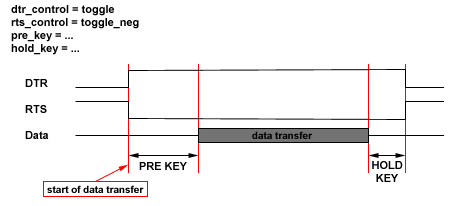
Behavior of DTR/RTS in the modes
toggle/toggle_neg | | dsr_sense | parameter determines if DSR is active at the high or low
level (high = positive handshake, low = negative
handshake). | | tx_continue_xon_xoff | enables stopping of transmission if the input buffer is full
and the character XOFF was sent (xoff_char). If true
is set, the transmission continues up to the moment when in the
input buffer contains at least xoff_tresh free
characters and the driver sent the XOFF character (xoff_char)
for pause receiving. If false is set, the transmission
does not continue up to the moment when in the input buffer contains
at least xon_tresh free characters and the driver sent
the XON character (xon_char) for restoration of
receipt. The default value is false. | | tx_xon_xoff | enables XON/XOFF (software) control for output. The default
value is false. | | rx_xon_xoff | enables XON/XOFF (software) control for input. The default
value is false. | | xon_tresh | the minimum free capacity of the input buffer for sending of
XON. The default value is 50 per cent. | | xoff_tresh | influences the maximum number of characters in the input
buffer for sending of XOFF. The maximum number of permitted
characters can be calculated by subtracting the shown value from the
input buffer size (rx_buffer) The default value is 80
per cent. | | error_xlat | enables replacement of the characters received with parity
error by the character err_char. If true is set and the
checking of parity is enabled, there is replacement. The default
value is false. | | discard_null | enables removal of empty (NULL) characters. If true
is set, each NULL character is removed from the input buffer
immediately after receipt. The default value is false. | | xon_char | decimal code of the character XON. | | xoff_char | decimal code of the character XOFF. | | err_char | decimal code of the character specified for replacement of
the characters received with parity error. | | eof_char | decimal code of the character EOF. | | evt_char | decimal code of the character EVT. | | rx_interchar_timeout | delay between individual characters for receipt in
milliseconds | | rx_char_timeout | timeout per one received character in milliseconds | | rx_timeout | constant timeout for receipt in milliseconds | | tx_char_timeout | timeout for sending of one character in
milliseconds. | | tx_timeout | constant timeout for sending in milliseconds |
Warning: The parameters rx_interchar_timeout,
rx_char_timeout and rx_timeout influence the
input throughput. By increasing the value rx_timeout it is
possible to achieve increase in efficiency for wide data transfers (it
is important to pay attention to the input buffer capacity), but will
also result in increased timeout between reception of separate blocks of
data. Setting the parameters to 0 instructs the system to use optimal
values based on the selected communication parameters. The
parameters tx_char_timeout and tx_timeout
influence the output throughput. Higher efficiency for large data
transfers, particularly with enabled handshake, can be obtained by
increasing the values. Too low values can cause transmission problems,
including relatively high number of failed transmission trials. Zero
parameter values cause setting of the optimum values according to the
communication parameters. Example of [comm] section parameters:
[comm]
baudrate=19200
parity=none
databits=8
stopbits=1
cts_flow=false
dsr_flow=false
dtr_control=high
rts_control=high
dsr_sense=low
rx_interchar_timeout=0
tx_char_timeout=0
rx_timeout=0
rx_char_timeout=0
tx_timeout=0
rx_buffer=1024
tx_buffer=1024
rx_frame_buffer=1024
tx_frame_buffer=1024
Driver channels
The Control Web application uses driver channels to write
messages to be sent to GSM device, to read received messages from
device and also to control the driver itself (to handle
exceptions, to obtain error code etc.).
Driver defines the following channels:
channel No.1 - real input - driver
exception status. Channel values and their meanings are
described in the chapter Driver
exceptions. channel No.2 - boolean output -
enables generation of the next driver exceptions. Writing of the
true value to this channel enables generation of
the next exception. channel No.3 - real input - error
code. Individual error codes are described in the chapter Error codes. channel No.4 - real input - number
of processed driver exceptions. channel No.5 - real input - number
of unhandled driver exceptions (exceptions in queue). channel No.6 - string output -
phone number, to which the message has to be sent. The number
format must comply with the rules required by the particular
modem. That means the country code may or may not be present in
the PDU mode, the leading "+" before country code must be
present in the text mode. This format is described in the
particular modem documentation. channel No.7 - string output - text
of the message to be sent. channel No.8 - boolean output -
send message command. Writing true to this channel
causes the message is actually sent to defined phone
number. channel No.9 - string input - phone
number from which the message was received. channel No.10 - string input - text
of the received message.
Driver procedures
The application may call for the driver certain
procedures using which it is possible to control the behavior of the
driver or to gain important information. This is done by means of the
system procedure: system.DriverQueryProc( DriverName : string; Param1 : any; &Param2 : any ) Parameters of the procedure have the following
meaning: | Parameter | Meaning |
|---|
| DriverName | symbolic name of the driver defined in the
application, | | Param1 | serves for typing of the command (name of the driver
procedure). | | Param2 | is used as a parameter of the procedure or the return value
of the procedure. |
DriverName and Param1 are typed as
text strings. Param2 is of various type according to the
meaning of the procedure. Some procedures serving for setting of
parameters may finish in error.
Overview and meaning of driver procedures (Param1 parameter)
- GetVersion
-
Returns in Param2 the string
describing the driver name and its version.
- GetMajorVersion
-
Returns version higher word of
the product Control Web.
- GetMinorVersion
-
Returns version lower word of
the product Control Web.
- GetAPIMajorVersion
-
Returns version higher word
of the API product Control Web.
- GetAPIMinorVersion
-
Returns version lower word
of the API product Control Web.
- EnableException
-
By calling this procedure the
further driver exception is permitted.
- GetErrorCode
-
Returns the error number of the
just processed driver exception.
See chapter Error codes for
details.
- GetExcStatus
-
Returns the just processed driver
exception code.
See chapter Driver
exceptions for details.
Driver Map File
Driver Map File (DMF) contains types of channels implemented in
this driver. This file is a part of driver definition within the
Control Web application. SMSDRV has a fixed set of channels so the
user should not modify SMS.MAP file supplied with the driver.
Content of driver map file.
begin
1 real input
2 boolean output
3 real input
4 real input
5 real input
6 string output
7 string output
8 boolean output
9 string input
10 string input
11 boolean input
12 real input
13 real input
14 real input
end.
Driver exceptions
The exception is raised when communication error appears. This
exception can be handled by any virtual instrument within the
application. The particular virtual instrument must define the
driver_exception parameter with the driver symbolic
name. In this case the instrument is activated when the exception
appears. It is necessary to write the true value to
the channel No. 2 or to invoke EnableException driver
procedure. This enables generation of next exception (if any). It
is possible to read channel No. 1 to obtain the exception state.
Keep on mind the send_same_data parameter must be set
to true if the instrument writes channel No. 2 (else
the next write of the same value will be discarded). If the
application does not handle exceptions, they are added to the
queue. Maximal queue length is defined by the parameter MaxExceptions
in the [Settings] section of driver parameter file
(PAR).
Exception status codes
0 = stReady — the
driver established connection with the modem (e.g. after
communication error). 1 = stError — communication error occurred. Either message
could not be sent or the modem does not respond to the
driver requests. 2 = stSMSData — new
text message was received.
Error codes
If some error occurs, en exception with code 3 (stError) is
raised. Error code is provided on the channel No. 3: If the error
condition occurs then an error message is also written to Log
Window of the Control Web.
0 — erOK,
success. 1 — erTimeout, timeout
error. 2 — erValue, invalid
value. 3 — erChannel,
non-existing channel.
1000 — erBusy, an attempt
to send text message before the previous send operation is
finished. 1001 — erSendSMS, send
text message operation failed. 1002 — erModem, modem does
not respond to the driver requests. The modem can switched off,
unplugged or battery can be drained etc.
Example of driver usage
There are several examples of the driver usage in the package
installation. These examples can be found in the
'EXAMPLES\SMSDRV' directory. Examples also contain
'*.DMF' and '*.PAR' files. It is necessary
to modify these files according to actual device
configuration.
|